Practice Essentials
Astrocytoma is the most common brain tumor (see image shown below), accounting for more than half of all primary CNS malignancies in children.
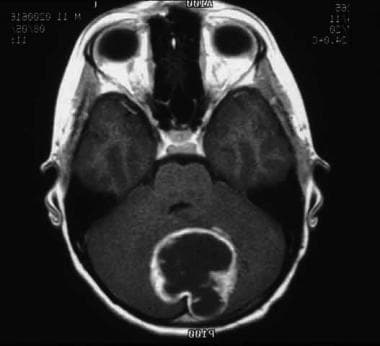
This MRI shows a pilocytic astrocytoma of the cerebellum.
Signs and symptoms of astrocytoma
Initial symptoms are usually nonspecific, nonlocalizing, and related to increased intracranial pressure (ICP). The classic triad of a raised ICP consists of the following:
Morning headaches
Vomiting
Lethargy
School-aged children more commonly report vague intermittent headaches and fatigue. Infants may present with irritability, anorexia, developmental delay, or regression.
Other signs and symptoms are related to the location of the tumor.
See Presentation for more detail.
Diagnosis of astrocytoma
The following studies are indicated in patients with suspected astrocytoma:
Head CT imaging with and without contrast
Head and spine MRI with and without gadolinium
CT imaging or MRI must be performed before the lumbar puncture to rule out hydrocephaly in those patients suspected of having a brain tumor. Cerebrospinal fluid cytologic examination is useful in malignant astrocytomas for the detection of microscopic leptomeningeal dissemination.
See Workup for more detail.
Management of astrocytoma
Treatment of astrocytomas depends on the location and grade of the tumor. Tumor location and associated morbidity may limit resection or render the tumor inoperable.
See Treatment and Medication for more detail.