Practice Essentials
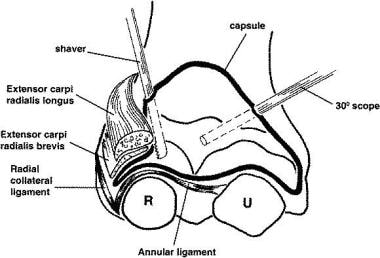
Lateral epicondylitis (commonly referred to as “tennis elbow”) is related to excessive wrist extension. It is the most common overuse syndrome. Patients typically report pain over the lateral elbow that worsens with activity and improves with rest. The symptoms tend to improve in 9-18 months; however, refractory cases may require surgery (see the image below).
Representation of the relationships in arthroscopic release for lateral epicondylitis.
Signs and symptoms of lateral epicondylitis
Pain generally occurs 24-72 hours after repeated wrist extension activity. Maximal tenderness on palpation is elicited 1-2 cm distal to the origin of the extensor carpi radialis brevis at the lateral epicondyle.
See Presentation for more detail.
Diagnosis of lateral epicondylitis
Imaging studies are rarely needed in the initial workup of lateral elbow pain. Consider plain film radiologic evaluation if the patient’s symptoms persist despite adequate treatment or to evaluate for osteophytes, degenerative joint disease, or osteochondritis dissecans (OCD). Consider magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), bone scanning, and/or computed tomography (CT) scanning to evaluate for OCD or stress fractures. Musculoskeletal ultrasonography is emerging as a useful modality to characterize areas of tendinosis, partial tearing, or calcifications and may assist with treatment options.
See Workup for more detail.
Treatment of lateral epicondylitis
Among the numerous treatment options are the following:
Watchful waiting
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Corticosteroid injection
Counterforce bracing
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy
Ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermal lesioning
Acupuncture
Autologous blood injection
Platelet-rich plasma injection
Hyaluronate injection
Polidocanol
Botulinum toxin
Topical nitrates
Bone marrow injection
Autologous tenocyte injection
Allogenic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Percutaneous tenotomy
High-intensity laser therapy
Surgical intervention can be very effective for refractory cases of lateral epicondylitis. However, surgical intervention is only indicated after 6 months of conservative care has failed to relieve symptoms.
See Treatment and Medication for more detail.