Overview
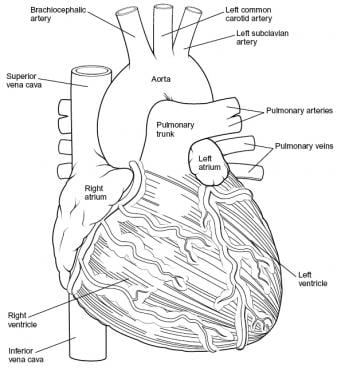
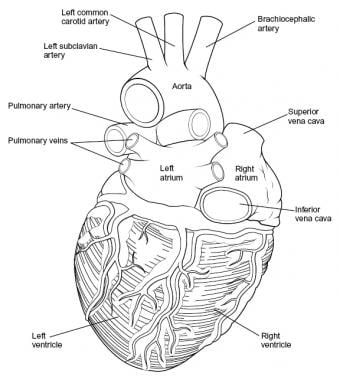
Intraoperatively, the anatomy of the heart is viewed from the right side of the supine patient via a median sternotomy incision. The structures initially seen from this perspective include the superior vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, and aorta. Medial displacement of the right side of the heart exposes the left atrium and right pulmonary veins. Medial rotation from the left exposes the left ventricle apex, left pulmonary veins, and left atrium. (See the images below.)
Heart, anterior view.
Heart, posterior view.
The overall shape and position of the heart may vary according to the relative size and orientation of each of its parts. For example, a large right ventricle may allow exposure of only a short segment of aorta; this is because of the narrow confines of the middle mediastinal space.