Overview
Embolization is useful in a broad spectrum of clinical situations. Embolization can be particularly effective in hemorrhage, regardless of whether the etiology is trauma, tumor, epistaxis, postoperative hemorrhage, or GI hemorrhage (see the images below). It can be performed anywhere in the body that a catheter can be placed, including the intracranial vasculature, head and neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and extremities. With the availability of coaxial microcatheters, superselective embolizations can be performed. In most patients, embolization for hemorrhage is preferable to surgical alternatives.
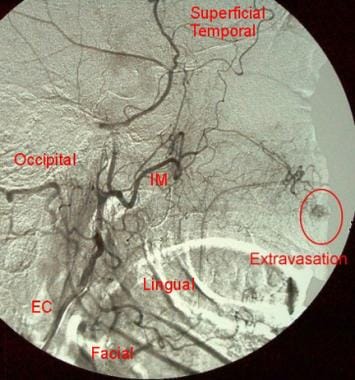
Digital-subtraction angiogram of the right external carotid artery (EC) in a 73-year-old woman with a 1-day history of epistaxis. This image demonstrates a suspicious blush of contrast off one branch of the internal maxillary artery (IM) within the highlighted area. Hemorrhage continued despite anterior and posterior nasal packing.
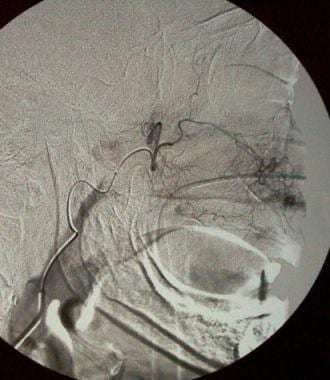
Digital-subtraction angiogram of the right internal maxillary artery in a 73-year-old woman with a 1-day history of epistaxis (same patient as in the previous image). This image confirms the area of blush and further demonstrates active extravasation from the sphenopalatine branch of the internal maxillary artery. A coaxial microcatheter was placed in the internal maxillary artery.
Postembolization digital-subtraction angiogram in a 73-year-old woman with a 1-day history of epistaxis (same patient as in the previous 2 images). This image demonstrates cessation of flow past the mid portion of the internal maxillary artery. The internal maxillary artery was embolized using polyvinyl alcohol. No further evidence of extravasation is seen.
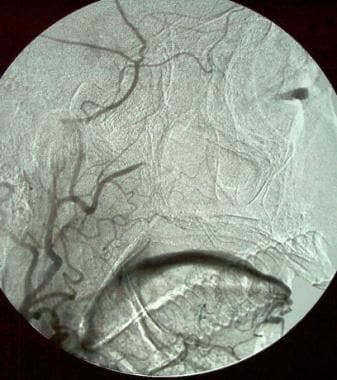
Bronchial artery embolization digital-subtraction angiogram of the right bronchial artery in a 46-year-old man with massive hemoptysis. Chest computed tomography scanning showed a consolidation of unknown etiology in the right upper lobe. Bronchoscopy confirmed the right upper lobe as the source of bleeding. The angiogram was performed with a Mikaelsson catheter in the descending thoracic aorta. The tip of the catheter is in the ostia to the right bronchial artery. The angiogram demonstrates an abnormally intense blush in the right upper lobe.
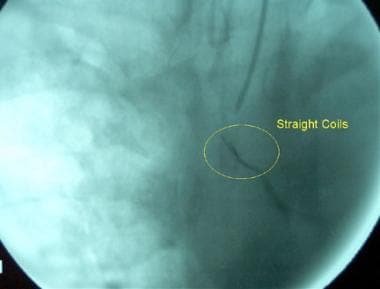
Bronchial artery postembolization digital-subtraction arteriogram in a 46-year-old man with massive hemoptysis (same patient as in the previous image). Four 1-cm straight coils were used to embolize the main trunk of the right bronchial artery. The arteriogram demonstrates complete embolization of the artery. The proximal trunk of the main artery is opacified.
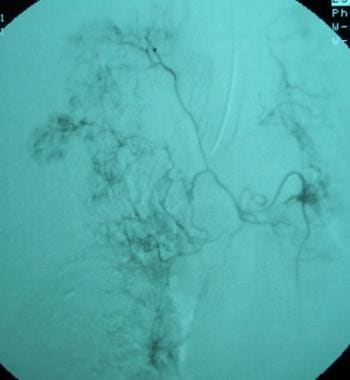
Bronchial artery embolization in a 46-year-old man with massive hemoptysis (same patient as in the previous 2 images). This arteriogram is an unsubtracted image of the previous image. The straight coils are demonstrated more clearly. The patient’s hemoptysis resolved postembolization.
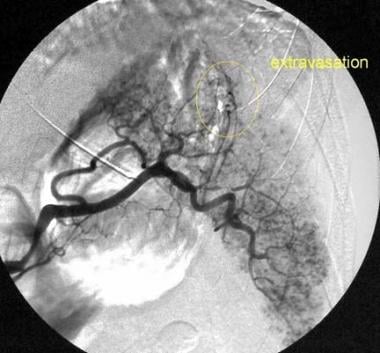
Splenic artery angiogram in a 32-year-old man who was an unrestrained passenger in a head-on motor vehicle accident (same patient as in the previous image). There are numerous small areas of contrast accumulation in the splenic parenchyma known as the “starry night” appearance, which is consistent with splenic injury. At the junction of the mid and superior poles, an area of active extravasation is highlighted within the circled area.
Patient Education
For patient education resources, see the Ear, Nose, and Throat Center and the Digestive System Center, as well as Nosebleeds and Gastrointestinal Bleeding.