Practice Essentials
Neuroblastoma is the most common extracranial pediatric neoplasm and the third most common pediatric malignancy after leukemia and central nervous system (CNS) tumors. In the first year of life, neuroblastoma accounts for 50% of all tumors.
Neuroblastoma is associated with a favorable prognosis, with most patients considered to be at low or intermediate risk for recurrence of the disease.
Neuroblastomas can arise from anywhere along the sympathetic chain. They have been associated with a number of disorders, such as Hirschsprung disease, fetal alcohol syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome, Von Recklinghausen disease, and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome.
CT scanning is the modality most commonly used to diagnose and stage neuroblastomas.
About 80-90% of neuroblastomas show stippled calcifications on CT. Intraspinal extension of neuroblastomas can be seen on radiographs. Intravenous pyelography (IVP) and excretory urography were widely used in the past to evaluate patients with adrenal neuroblastomas before the advent of computed tomography (CT), MRI, and ultrasonography.
MRI has some advantages over CT,
such as no need for ionizing radiation; multiplanar imaging capabilities; and, often, the elimination of the need for IV contrast enhancement.
Obstetric ultrasonography can depict fetal neuroblastomas as early as 19 weeks’ gestational age. Most of the cases identified during obstetric ultrasonography are diagnosed during the third trimester (around 36 weeks).
The radiologic characteristics of neuroblastomas are demonstrated in the images below.
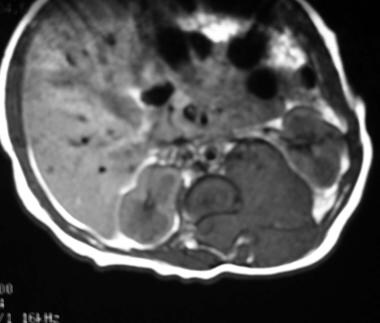
Axial nonenhanced T1-weighted MRI shows a hypointense mass in the retroperitoneum originating from the left adrenal gland. The mass displaces the left kidney in an anterolateral direction, it extends through the neuroforamen into the spinal canal, and it displaces the spinal cord to the right. The exact site of origin of large masses can be difficult to determine. Sympathetic-chain primaries supposedly invade the spinal canal with greater frequency than do adrenal primaries.
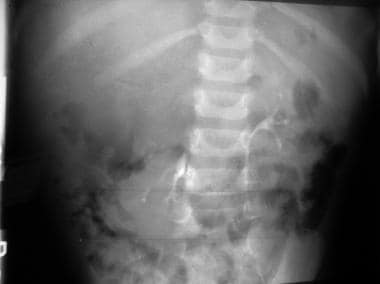
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) shows an inferiorly displaced kidney on the right. Above the right kidney are stippled calcifications. These findings are consistent with those of a neuroblastoma.
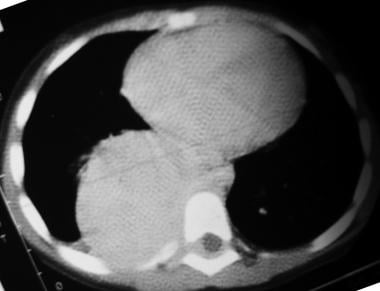
Nonenhanced axial CT scan of the chest in a patient with a thoracic neuroblastoma shows a large, right posterior mediastinal mass extending into the spinal canal and displacing the cord laterally to the left.