Background
The association of anemia and gastrointestinal and neurologic abnormalities referable to the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves has been recognized in several clinical and postmortem case reports and series by Combe, Addison, and Fenwick since the early 19th century. In 1877, Gardner and Osler coined the term pernicious anemia (PA) to describe a patient with progressive arm numbness and difficulty with buttoning and using tools.
Liechtenstein in 1884 reported the association of PA and spinal cord disease but attributed both to tabes dorsalis.
Lichtheim in 1887
and Minnich in 1892
recognized the histologic differences in the spinal cord between PA and tabes dorsalis.
In 1900, Russell et al coined the term subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord.
In 1926, Minot and Murphy fed PA patients a half-pound of calf liver daily, for which they received the Nobel Prize.
In 1929, Castle distinguished the role of gastric (intrinsic) and dietary (extrinsic) factors in PA.
In 1948, cyanocobalamin was isolated from the liver. The existence of vitamin B-12 deficiency neuropathy was recognized in 1958. In 1955, Lassen et al
noted megaloblastic anemia secondary to prolonged nitrous oxide (N2 O) exposure; the neurologic features were described in 1978 by Sahenk et al
and Layzer et al.
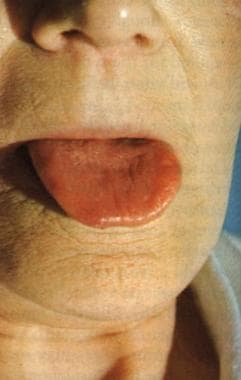
See the image below.
Vitamin B-12–associated neurological diseases. Pernicious anemia. Characteristic lemon-yellow pallor with raw beef tongue lacking filiform papillae. Photo from Forbes and Jackson with permission.
See 21 Hidden Clues to Diagnosing Nutritional Deficiencies, a Critical Images slideshow, to help identify clues to conditions associated with malnutrition.